Node-type fields specifications
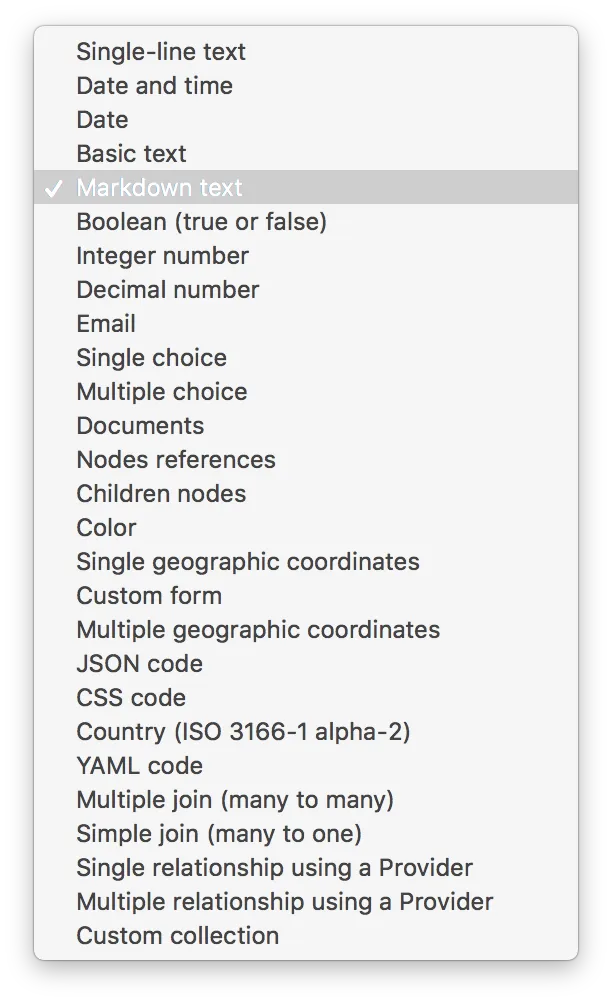
Roadiz can handle many types of node-type fields. Here is a complete list:
TIP
- Title, meta-title, meta-description, and keywords are always available since they are stored directly inside the
NodesSourcesentity. This ensures that you will always have a title no matter the node-type you are using.
Simple data
The following fields store simple data in your custom node-source database table.
| Single-line text | string |
| Date | date |
| Date and time | date-time |
| Basic long text | text |
| Markdown text | markdown |
| Boolean | boolean |
| Integer number | integer |
| Decimal number | decimal |
email | |
| Colour | colour |
| Single geographic coordinates | geographic.coordinates |
| Multiple geographic coordinates | multiple.geographic.coordinates |
| JSON code | json |
| CSS code | css |
| Country code (ISO 3166-1 alpha-2) | country |
| YAML code | yaml |
| Many to many join | many-to-many |
| Many to one join | many-to-one |
| Single relationship using a provider | single-provider |
| Multiple relationship using a provider | multiple-provider |
| Custom collection | collection |
Single and multiple geographic coordinates
Geographic coordinates are stored in JSON format in your database using the GeoJSON schema:
- A single point will be stored as a GeoJSON feature to hold additional properties such as zoom.
- Multiple points will be stored as a GeoJSON feature collection.
By default, the Roadiz back office uses the Leaflet library with Open Street Map for tile rendering and basic geocoding features.
Markdown options
You can restrict Markdown fields buttons using the following YAML configuration:
allow_h2: false
allow_h3: false
allow_h4: false
allow_h5: false
allow_h6: false
allow_bold: false
allow_italic: false
allow_blockquote: false
allow_list: false
allow_nbsp: false
allow_nb_hyphen: false
allow_image: false
allow_return: false
allow_link: false
allow_hr: false
allow_preview: false
allow_translate_assistant_translate: false
allow_translate_assistant_rephrase: falseallow_translate_assistant_translate and allow_translate_assistant_rephrase add control to the Translate Assistant. Translate Assistant
Virtual data
Virtual types do not store data in the node-source table. They display custom widgets in your editing page to link documents, nodes, or custom-forms with your node-source.
- Documents:
documents - Nodes references:
nodes - Custom form:
custom-forms
Complex data
These field types must be created with default values (comma-separated) to display available default choices for "select-box" types:
- Single choice:
single-choice - Multiple choices:
multiple-choice - Children nodes:
children-nodes
The Children node field type is a special virtual field that displays a custom node-tree inside your editing page. You can add quick-create buttons by listing your node-types names in the default values input, comma-separated.
Universal fields
If you need a field to hold exactly the same data for all translations, you can set it as universal. For example, for documents, numeric, and boolean data that do not change from one language to another.
It will duplicate data at each save time from the default translation to others. It will also hide the edit field from non-default translations to avoid confusion.
YAML field
When you use the YAML field type, you get an additional method to return your code already parsed. If your field is named data, your methods will be generated in your NSEntity as getData() and getDataAsObject().
getData()method will return your YAML code as a string.getDataAsObject()will return mixed data, array, orstdObjectaccording to your code formatting. This method will throw a\Symfony\Component\Yaml\Exception\ParseExceptionif your YAML code is not valid.
Many to many and Many to one joins
You can create custom relations between your node-source and whatever Doctrine entities in Roadiz or in your theme.
You must fill the default values field for these two types.
# Entity class name
classname: App\Entity\City
# Displayable is the method used to display entity name
displayable: getName
# Same as Displayable but for a secondary information
alt_displayable: getZipCode
# Optional: you can specify an inversedBy relation if you want your App\Entity\City object to be able to access its nodes-sources
# You will have to add attribute: #[ORM\OneToMany(mappedBy: 'yourFieldName', targetEntity: NSYourType::class)]
inversed_by: nodesSources
# Searchable entity fields
searchable:
- name
- slug
orderBy:
- field: slug
direction: ASCProxied many-to-many relation
You can use a custom proxy entity to support persisting position on your relation.
Roadiz will generate a one-to-many relationship with the proxy entity instead of a many-to-many.
In this scenario, you are responsible for creating and migrating App\Entity\PositionedCity entity.
If you are migrating from a non-proxied many-to-many relation, you should keep the same table and field names to keep data intact.
# Entity class name
classname: App\Entity\City
# Displayable is the method used to display entity name
displayable: getName
# Same as Displayable but for a secondary information
alt_displayable: getZipCode
# Searchable entity fields
searchable:
- name
- slug
# This order will only be used for explorer
orderBy:
- field: slug
direction: ASC
# Use a proxy entity
proxy:
classname: App\Entity\PositionedCity
self: nodeSource
relation: city
# This order will preserve position
orderBy:
- field: position
direction: ASCSingle and multiple provider
The generic provider type allows you to fetch every data you want through a Provider class in your theme. This can be really useful if you need to fetch items from an external API and reference them in your nodes-sources.
Imagine that you want to link your page with an Instagram post. You’ll have to create a class that extends RZ\Roadiz\RozierBundle\Explorer\AbstractExplorerProvider (with #[AutoconfigureTag('roadiz.explorer_provider')]) and configure it in your field:
classname: App\Provider\ExternalApiProviderThis provider will implement getItems, getItemsById, and other methods from ExplorerProviderInterface to display your Instagram posts in the Roadiz explorer widget and find your selected items back. Each Instagram post will be wrapped in a RZ\Roadiz\RozierBundle\Explorer\AbstractExplorerItem that maps your custom data to the right fields to be shown in the Roadiz back office.
You’ll find an implementation example in Roadiz with RZ\Roadiz\RozierBundle\Explorer\SettingsProvider and RZ\Roadiz\RozierBundle\Explorer\SettingExplorerItem. These classes do not fetch data from an API but from your database using EntityListManager.
Single and multiple provider types can accept additional options too. If you want to make your provider configurable at runtime, you can pass options in your field configuration.
classname: App\Provider\ExternalApiProvider
options:
- name: user
value: me
- name: access_token
value: xxxxxThen you must override your provider’s configureOptions method to add which options are allowed.
use Symfony\Component\OptionsResolver\OptionsResolver;
/**
* @param OptionsResolver $resolver
*/
public function configureOptions(OptionsResolver $resolver)
{
$resolver->setDefaults([
'page' => 1,
'search' => null,
'itemPerPage' => 30,
// add more default options here
'user' => 'me',
]);
// You can require options
$resolver->setRequired('access_token');
}Custom collection
Last but not least, you can create a custom collection field to store read-only data using a dedicated Symfony AbstractType.
You must fill the default values field for this type:
# AbstractType class name
entry_type: App\Form\FooBarTypeYou must understand that custom collection data will be stored as a JSON array in your database. So you won’t be able to query your node-source using this data.
In your FooBarType, you’ll be able to use Symfony standard field types and Roadiz non-virtual fields too, such as MarkdownType, JsonType, and YamlType.
